Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition brought on by increased pressure on the median nerve at the wrist. In effect, it is a pinched nerve at the wrist. Symptoms may include numbness, tingling, and pain in the arm, hand, and fingers. There is a space in the wrist called the carpal tunnel where the median nerve and nine tendons pass from the forearm into the hand (see Figure 1). Carpal tunnel syndrome happens when pressure builds up from swelling in this tunnel and puts pressure on the nerve. When the pressure from the swelling becomes great enough to disturb the way the nerve works, numbness, tingling, and pain may be felt in the hand and fingers (see Figure 2).
What causes carpal tunnel syndrome?
Usually the cause is unknown. Pressure on the nerve can happen several ways: swelling of the lining of the flexor tendons, called tenosynovitis; joint dislocations, fractures, and arthritis can narrow the tunnel; and keeping the wrist bent for long periods of time. Fluid retention during pregnancy can cause swelling in the tunnel and symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, which often go away after delivery. Thyroid conditions, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes also can be associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. There may be a combination of causes.
Signs and symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms usually include pain, numbness, tingling, or a combination of the three. The numbness or tingling most often takes place in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers. The symptoms usually are felt during the night but also may be noticed during daily activities such as driving or reading a newspaper. Patients may sometimes notice a weaker grip, occasional clumsiness, and a tendency to drop things. In severe cases, sensation may be permanently lost and the muscles at the base of the thumb slowly shrink (thenaratrophy), causing difficulty with pinch.
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
A detailed history including medical conditions, how the hands have been used, and whether there were any prior injuries is important. An x-ray may be taken to check for the other causes of the complaints such as arthritis or a fracture. In some cases, laboratory tests may be done if there is a suspected medical condition that is associated with CTS. A nerve conduction study (NCV) and/or electromyogram (EMG) may be done to confirm the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome as well as to check for other possible nerve problems.
Treatment of carpal tunel syndrome
Symptoms may often be relieved without surgery. Identifying and treating medical conditions, changing the patterns of hand use, or keeping the wrist splinted in a straight position may help reduce pressure on the nerve. Wearing wrist splints at night may relieve the symptoms that interfere with sleep. A steroid injection into the carpal tunnel may help relieve the symptoms by reducing swelling around the nerve.
When symptoms are severe or do not improve, surgery may be needed to make more room for the nerve. Pressure on the nerve is decreased by cutting the ligament that forms the roof (top) of the tunnel on the palm side of the hand (see Figure 3). Incisions for this surgery may vary, but the goal is the same: to enlarge the tunnel and decrease pressure on the nerve. Following surgery, soreness around the incision may last for several weeks or months. The numbness and tingling may disappear quickly or slowly. It may take several months for strength in the hand and wrist to return to normal. Carpal tunnel symptoms may not completely go away after surgery, especially in severe cases.
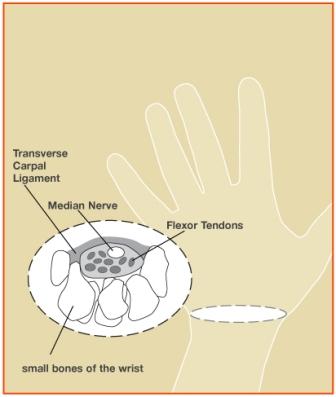
Figure 1: The carpal tunnel is found at the base of the palm. It is formed by the bones of the wrist and the transverse carpal ligament. Increased pressure in the tunnel affects the function of the median nerve.
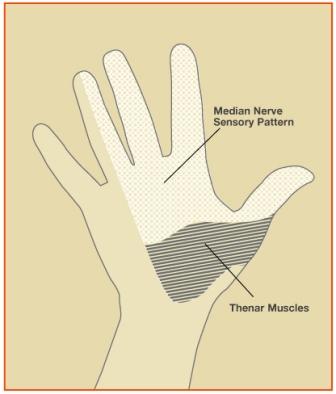
Figure 2: Aspects of median nerve function.
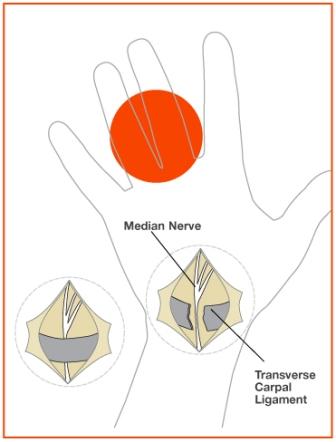
Figure 3: The goal of surgery is to free the ligament to allow more room for the median nerve in the carpal tunnel.
© 2006 American Society for Surgery of the Hand
|



